반응형

구조
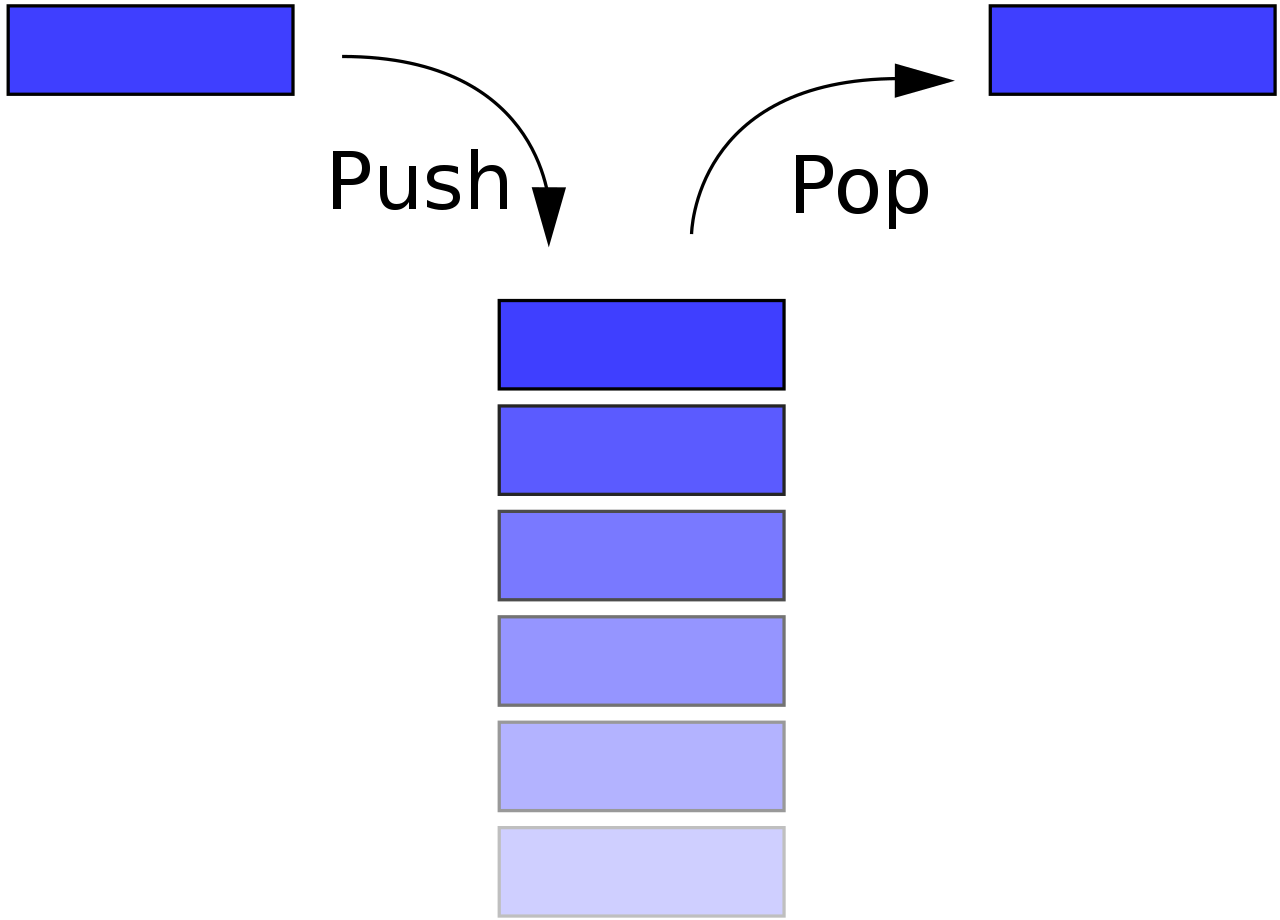
스택(stack)은 제한적으로 접근할 수 있는 나열 구조이다. 그 접근 방법은 언제나 목록의 끝에서만 일어난다.
끝먼저내기 목록(Pushdown list)이라고도 한다.
스택은 한 쪽 끝에서만 자료를 넣거나 뺄 수 있는 선형 구조(LIFO - Last In First Out)으로 되어 있다.
자료를 넣는 것을 '밀어넣는다' 하여 푸쉬(push)라고 하고 반대로 넣어둔 자료를 꺼내는 것을 팝(pop)이라고 하는데,
이때 꺼내지는 자료는 가장 최근에 푸쉬한 자료부터 나오게 된다.
이처럼 나중에 넣은 값이 먼저 나오는 것을 LIFO 구조라고 한다.
이를테면, a부터 b와 c를 순서대로 넣은 다음 자료를 하나씩 꺼내면 c부터 b와 a의 순서로 나오게 된다.
구현 코드
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
static class Stack {
int[] array;
int cursor = 0;
Stack(int size) {
array = new int[size];
}
void push(int number) {
if (array.length <= cursor) {
System.out.println("Overflow");
} else {
array[cursor++] = number;
}
}
void pop() {
if (cursor == 0) {
System.out.println("Underflow");
} else {
cursor--;
}
}
void top() {
if (cursor == 0) {
System.out.println("NULL");
} else {
System.out.println(array[cursor - 1]);
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in);
String[] init = scan.nextLine().split(" ");
int size = Integer.parseInt(init[0]);
int loopCnt = Integer.parseInt(init[1]);
Stack stack = new Stack(size);
for (int i = 0; i < loopCnt; i++) {
String[] commands = scan.nextLine().split(" ");
int cmd = Integer.parseInt(commands[0]);
int num = 0;
if (commands.length > 1) {
num = Integer.parseInt(commands[1]);
}
if (cmd == 1) {
stack.push(num);
} else if (cmd == 2) {
stack.pop();
} else if (cmd == 3) {
stack.top();
}
}
}
}
참고 문서
스택 - 위키백과, 우리 모두의 백과사전 - https://ko.wikipedia.org/wiki/스택
반응형